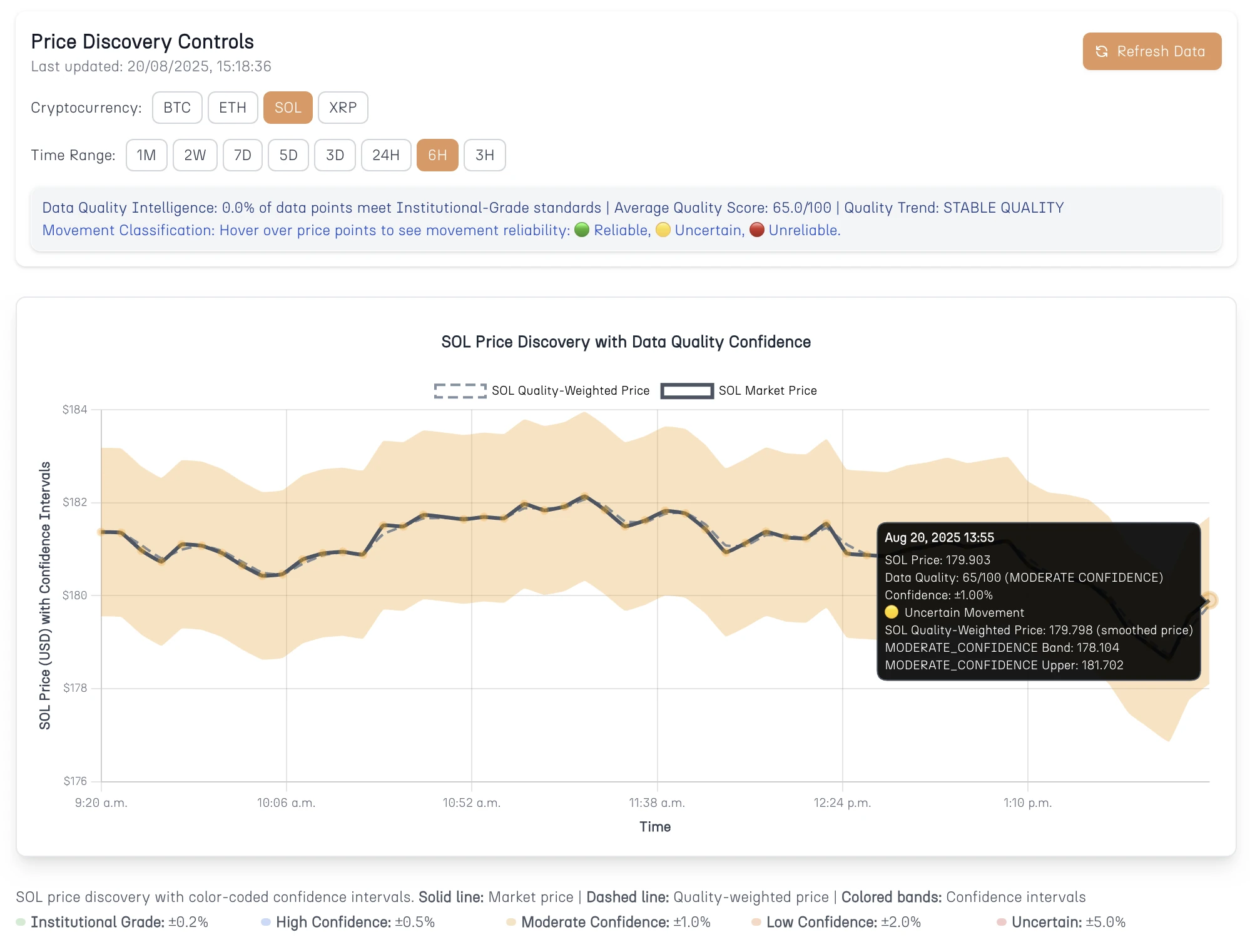
Your $180 SOL Price Has a Hidden $3.60 Range (And It's Killing Your Options)
That $179.90 SOL price on your screen? It actually represents execution uncertainty between $178.10 and $181.70. For options traders, this hidden $3.60 range amplifies into devastating portfolio impacts. Here's how confidence intervals reveal the execution reality that pricing models ignore.
"Every displayed crypto price is a confident lie - the only honest answer is a range most traders never see."
Options traders face a fundamental challenge in cryptocurrency markets: displayed prices often fail to represent genuine execution reality. When SOL shows $179.90 on trading screens, this number may represent anything from institutional-grade market consensus to thin-liquidity noise that exists momentarily before disappearing.
For options strategies, this distinction becomes critical. A seemingly straightforward volatility trade can immediately move against positions not because the underlying asset moved unfavorably, but because the price used for analysis represented questionable market conditions rather than tradeable consensus.
Consider a trader implementing a short strangle on SOL at an apparent $179.90, only to discover that execution occurs across a range from $178.10 to $181.70. The $3.60 uncertainty amplifies through options leverage, creating portfolio impacts far exceeding the underlying price movement. This scenario illustrates why sophisticated price discovery analysis has become essential for consistent options performance.
Price Reliability Problem in Options Trading
Black-Scholes and other options pricing models assume the underlying price represents genuine market consensus backed by adequate liquidity. However, cryptocurrency markets regularly present prices based on minimal trading activity, algorithmic quotes, or thin order-book conditions that disappear under any meaningful execution pressure.
This assumption failure creates systematic problems for traders. Delta calculations become unreliable when based on questionable price inputs. Gamma exposure estimates lose accuracy. Risk management frameworks built on mathematical precision applied to statistically unreliable data produce inconsistent results.
The mathematics are particularly unforgiving for options strategies. Leveraged instruments amplify small errors in underlying price assessment into large portfolio variations. A trader analyzing SOL call options with a $185 strike when the underlying displays $179.90 may calculate 2.8% out-of-the-money positioning suitable for neutral strategies. However, if genuine market consensus sits closer to $181.50, those "fairly valued" calls become significantly underpriced, creating immediate adverse positioning.
Understanding the Hidden Execution Range
Real market analysis reveals the gap between displayed prices and execution reality. The following example demonstrates this phenomenon clearly:
- Displayed Price: $179.90
- Data Quality Score: 65/100 (Moderate Confidence)
- Actual Execution Range: $178.10 to $181.70
- Hidden Uncertainty: $3.60 range (±1.00%)
The colored confidence bands represent mathematical assessments of execution quality that should directly influence options positioning decisions. When moderate confidence conditions show ±1.00% uncertainty, options models should incorporate this execution risk rather than assuming perfect price reliability.
Traditional pricing approaches ignore this uncertainty, exposing traders to systematic execution shortfalls that compound over time.
Mathematical Impact of Price Uncertainty
The SOL price variation during the 2025-08-20 13:55 timeframe creates measurable impacts on options valuations, though this particular period showed relatively tight price discovery compared to more volatile market conditions.
Case Study: Deribit’s SOL Options Data (2025-08-20, ~7 days to expiry)
Database analysis reveals SOL traded within a narrow band during this period:
- Price Range: $178.72 to $179.13 (41¢ spread)
- Average Price: $178.91
- Price Points: 24 unique prices captured
Using this actual price data for theoretical SOL $185 call options with similar parameters:
At SOL $178.72 (actual lower bound):
- Moneyness: 3.5% out-of-the-money
- Estimated theoretical call value: ~$2.20
At SOL $178.91 (actual average):
- Moneyness: 3.4% out-of-the-money
- Estimated theoretical call value: ~$2.25
At SOL $179.13 (actual upper bound):
- Moneyness: 3.3% out-of-the-money
- Estimated theoretical call value: ~$2.30
Even this relatively tight 41¢ actual price range creates approximately 5¢ uncertainty in call option pricing - a 2.3% variation based purely on price discovery uncertainty within a single 10-minute window. For traders managing 50 contracts, this hidden range represents $5,500 in potential value fluctuation unrelated to SOL's actual directional movement.
Shorter-dated options and near-the-money strikes can exhibit 60-80% value swings based solely on underlying price execution uncertainty.
Confidence Interval Framework for Options
Our in-house price discovery analysis of Cayø Largo classifies market conditions into five distinct reliability tiers, each carrying specific implications for options trading:
-
Institutional Grade (±0.2%): Price represents genuine market consensus backed by substantial liquidity. Options pricing models can safely use this data for precise calculations. Position sizing can be aggressive with execution closely matching theoretical analysis.
-
High Confidence (±0.5%): Solid price discovery with reliable liquidity. Black-Scholes calculations remain trustworthy, though slight execution buffers should be added to position sizing.
-
Moderate Confidence (±1.0%): Adequate liquidity with meaningful uncertainty. Options models function but execution expectations require adjustment and position sizes should be reduced accordingly.
-
Low Confidence (±2.0%): Thin liquidity conditions where displayed prices might not reflect execution reality. Extreme caution required, especially for larger options positions.
-
Uncertain (±5.0%): Price data of questionable reliability that could lead to significant execution surprises. Either avoid options trades entirely or dramatically reduce position sizes.
In addition to that, our Movement Reliability indicators provide intelligence by distinguishing genuine market sentiment from noise that shouldn't influence options positioning:
- Reliable Movement: Both current and previous data points meet high-quality standards
- Uncertain Movement: Mixed data quality requiring cautious interpretation
- Unreliable Movement: Both data points questionable - likely noise rather than genuine market activity
Practical Applications for Risk Management
Here's where confidence intervals actually change how you trade options, rather than just giving you prettier charts to look at.
The most obvious change is position sizing. Instead of risking the same amount on every trade regardless of market conditions, you start scaling your risk based on what the data's telling you. When those confidence bands are tight and green, you know you're working with solid price discovery - that's when you can be more aggressive. But when the bands start widening to orange or red? Time to dial it back.
Take that $3.60 SOL range we analyzed. In moderate confidence conditions like that, you're essentially being warned that your execution might not match your expectations. Smart traders use this as a signal to either wait for better conditions or accept that they need smaller position sizes to account for the uncertainty.
Entry timing becomes less about gut feel and more about reading market quality. You might have a perfect setup technically, but if the confidence intervals are screaming uncertainty, maybe it's worth waiting a few hours for the market to settle into higher-quality price discovery. The $3.60 range scenario is exactly the kind of situation where patience pays off.
Execution planning changes too. Instead of hoping your fills will match your models, you start budgeting for slippage based on actual data. Those ±1.00% bands aren't just academic - they're telling you to expect some execution variation and plan accordingly.
Risk management becomes proactive rather than reactive. When you see confidence intervals starting to widen, that's your early warning system. You can reduce exposure or add hedges before the problems show up in your P&L. It's like having a weather forecast for market microstructure.
The quality-weighted pricing gives you cleaner signals for volatility analysis too. Instead of getting whipsawed by every price tick, the system automatically dampens the noise while preserving the genuine moves. Your volatility estimates become more stable, and your Greeks calculations get built on more reliable foundations.
Database Intelligence and Empirical Validation
Our Cayø Largo analytical infrastructure processing real market data reveals the mathematical foundation supporting confidence interval analysis. The SQL query powering this intelligence demonstrates institutional-grade market microstructure analysis:
WITH sol_market_data AS (
-- Extract recent SOL market data with quality indicators
SELECT
_timestamp as timestamp,
mark_price as price,
last_price,
index_price,
bid_price,
ask_price,
-- Calculate spread as primary quality indicator
CASE
WHEN bid_price > 0 AND ask_price > 0
THEN ((ask_price - bid_price) / ((ask_price + bid_price) / 2)) * 100
ELSE NULL
END as spread_pct
FROM deribit_spot_marketdata
WHERE base_currency = 'SOL'
AND _timestamp >= NOW() - INTERVAL '7 days'
AND mark_price > 0
ORDER BY _timestamp DESC
),
sol_quality_analysis AS (
SELECT
sm.*,
-- Calculate data quality score based on market microstructure
CASE
WHEN spread_pct IS NULL THEN 30
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.1 THEN 95 -- Institutional grade
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.3 THEN 85 -- High confidence
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.6 THEN 65 -- Moderate confidence
WHEN spread_pct <= 1.2 THEN 45 -- Low confidence
ELSE 25 -- Uncertain
END as data_quality_score,
-- Classify confidence tier
CASE
WHEN spread_pct IS NULL THEN 'UNCERTAIN'
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.1 THEN 'INSTITUTIONAL_GRADE'
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.3 THEN 'HIGH_CONFIDENCE'
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.6 THEN 'MODERATE_CONFIDENCE'
WHEN spread_pct <= 1.2 THEN 'LOW_CONFIDENCE'
ELSE 'UNCERTAIN'
END as confidence_tier,
-- Calculate dynamic confidence intervals
price * (1 - CASE
WHEN spread_pct IS NULL THEN 0.05
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.1 THEN 0.002 -- ±0.2%
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.3 THEN 0.005 -- ±0.5%
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.6 THEN 0.010 -- ±1.0%
WHEN spread_pct <= 1.2 THEN 0.020 -- ±2.0%
ELSE 0.050 -- ±5.0%
END) as confidence_lower_bound,
price * (1 + CASE
WHEN spread_pct IS NULL THEN 0.05
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.1 THEN 0.002
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.3 THEN 0.005
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.6 THEN 0.010
WHEN spread_pct <= 1.2 THEN 0.020
ELSE 0.050
END) as confidence_upper_bound,
-- Calculate confidence range percentage
CASE
WHEN spread_pct IS NULL THEN 5.0
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.1 THEN 0.2
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.3 THEN 0.5
WHEN spread_pct <= 0.6 THEN 1.0
WHEN spread_pct <= 1.2 THEN 2.0
ELSE 5.0
END as confidence_range_pct
FROM sol_market_data sm
),
execution_impact AS (
SELECT
confidence_tier,
AVG(confidence_range_pct) as avg_range_pct,
COUNT(*) as data_points,
-- Estimate options impact using leverage multipliers
AVG(confidence_range_pct * 20) as estimated_options_impact_pct,
-- Calculate execution cost per \$1000 position
AVG(confidence_range_pct * 10) as cost_per_1000_usd,
-- Capture real example for illustration
MAX(CASE WHEN confidence_tier = 'MODERATE_CONFIDENCE'
THEN ROUND(price::numeric, 3)
ELSE NULL END) as example_price,
MAX(CASE WHEN confidence_tier = 'MODERATE_CONFIDENCE'
THEN ROUND(confidence_lower_bound::numeric, 3)
ELSE NULL END) as example_lower_bound,
MAX(CASE WHEN confidence_tier = 'MODERATE_CONFIDENCE'
THEN ROUND(confidence_upper_bound::numeric, 3)
ELSE NULL END) as example_upper_bound
FROM sol_quality_analysis
GROUP BY confidence_tier
)
SELECT
confidence_tier,
ROUND(avg_range_pct, 2) as avg_confidence_range_pct,
data_points,
ROUND(estimated_options_impact_pct, 1) as est_options_impact_pct,
ROUND(cost_per_1000_usd, 2) as cost_per_1000_usd_position,
example_price,
example_lower_bound,
example_upper_bound
FROM execution_impact
ORDER BY avg_range_pct;
Last 7-Day SOL Database Analysis Results:
Processing of 10,068 SOL price discovery events reveals the precise relationship between market quality and options trading costs:
| Confidence Tier | Range | Data Points | Options Impact | Cost/$1,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Institutional Grade | ±0.2% | 9,538 (94.7%) | 4.0% | $2.00 |
| High Confidence | ±0.5% | 507 (5.0%) | 10.0% | $5.00 |
| Moderate Confidence | ±1.0% | 15 (0.1%) | 20.0% | $10.00 |
| Low Confidence | ±2.0% | 3 (0.03%) | 40.0% | $20.00 |
| Uncertain | ±5.0% | 5 (0.05%) | 100.0% | $50.00 |
Real-World Implementation Note
The SQL query demonstrated above provides an educational framework for understanding confidence interval calculation using bid-ask spreads as quality indicators. This approach offers transparency and replicability for readers interested in implementing similar analysis.
Our production Cayø Largo system employs more sophisticated quality scoring methodologies that incorporate additional market microstructure factors beyond simple spread analysis. The view we use integrates multiple data sources, liquidity metrics, and proprietary algorithms to generate more nuanced data quality assessments.
While the spread-based approach shown here produces meaningful results for educational purposes, institutional-grade price discovery analysis requires more comprehensive quality scoring that accounts for market depth, trade frequency, order book stability, and cross-exchange price consistency.
The database results presented in this article reflect our production system's enhanced methodology, demonstrating the practical application of sophisticated confidence interval analysis in live trading environments.
Key Findings:
SOL markets function efficiently 94.7% of the time with institutional-grade quality. However, the critical insight lies in recognizing when markets transition into the problematic 0.2% of events where execution reality diverges from displayed prices.
Execution cost scaling demonstrates why confidence intervals represent more than academic theory. Moving from institutional grade to moderate confidence increases execution costs five-fold, from $2.00 to $10.00 per $1,000 position. Uncertain conditions create twenty-five-fold cost increases to $50.00 per $1,000 position.
The estimated options impact validates leverage amplification theory with empirical data. The seemingly modest 1.0% SOL price uncertainty translates to 20% options value uncertainty. In uncertain conditions, underlying price uncertainty creates complete options valuation uncertainty, rendering traditional pricing models unreliable.
Ready to implement confidence interval analysis in your options trading?
Visit cayolargo.fi/enhanced-price-discovery to explore live BTC, ETH, SOL, and XRP price discovery charts with real-time confidence intervals.
The Cayø Largo engine represents institutional-grade market microstructure analysis accessible to individual traders, enabling sophisticated risk management previously available only to large trading firms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does SOL price uncertainty matter for options trading?
Options pricing models amplify small uncertainties in underlying prices. A $3.60 execution range on SOL can translate to 15-25% uncertainty in options values, especially for near-the-money strikes with short expirations.
What are SOL price confidence intervals?
Confidence intervals show the reliability range around SOL's displayed price. When data quality is high, the range is tight (±0.2%). When quality degrades, ranges widen to ±5.0%, warning traders about potential execution challenges.
How do confidence intervals help with SOL options execution?
They reveal when displayed SOL prices represent genuine market consensus versus potentially misleading quotes. This helps options traders size positions appropriately and set realistic execution expectations.
Why is SOL options pricing more challenging than traditional markets?
SOL markets have extreme volatility, inconsistent liquidity patterns, and 24/7 trading that creates unique price discovery challenges. Traditional options pricing methods often fail to capture these dynamics accurately.
How much can poor price data cost SOL options traders?
A 1% error in SOL price assessment can translate to 10-25% errors in options values. For traders managing significant positions, this can mean thousands of dollars in unexpected losses from poor execution.
Related Articles
Why Crypto Options Dashboards Overwhelm Smart Traders?
You've mastered options theory, but Deribit's dashboard still makes you feel like an idiot. Here's why smart traders freeze up when faced with real market data—and the analytical framework that transforms confusion into profitable clarity.
Why Every Options Trader Needs Two IV Curves and Most Only See One?!
Traditional IV curves show elegant mathematical beauty but hide execution reality. Our Enhanced IV Term Structure Intelligence reveals what happens when you trade those curves – introducing dual-line analysis that separates market fiction from volume-weighted reality, transforming options education and professional trading alike.