Tail Strike™: Detecting What 25-Delta Skew Misses
Traditional 25-delta skew misses half the story in crypto options markets. We built Tail Strike™ to detect when institutional money accelerates into extreme strikes, catching tail events before they materialize.
October 10, 2025. Bitcoin trades around $122,000 level (Figure 1). Traditional 25-delta skew reads 2 to 3 points, slightly elevated but unremarkable for crypto volatility. Most analytics platforms call it standard put hedging. Market participants see modest bearishness, business as usual.
But something else was happening. Deep out-of-the-money puts, strikes 15-20% below spot, commenced accumulating at velocities far exceeding moderate strike buildups well before 14:00 UTC+2 (Figure 1). Institutional players most probably were constructing tail positions that traditional metrics couldn't distinguish from routine hedging. Within hours, Bitcoin dropped toward $110,000. That move caught traders off guard. They could position better than that. How?
By watching Tail Strike™ instead.
When Traditional Metrics Stop Working
Traditional options analytics emerged from equity markets where certain assumptions hold true. Stocks crash down more violently than they rally up. Trading happens during business hours, giving market participants time to rebalance overnight. Delta reference points remain stable for days or weeks. Volatility regimes shift gradually, measured in months.
Crypto obliterates every assumption. Bitcoin can crash 7%+ downward or explode 7%+ upward with equal ferocity on a Sunday morning. Options at moderate strikes can shift dramatically into deep tail or near-the-money territory within a single trading session following a 7% price move. Markets never close, eliminating reset cycles. Volatility regimes flip in hours, not months!
The mathematical definition of 25-delta skew is straightforward enough:
where represents implied volatility for puts at 25-delta, and for calls at the same delta. The measurement tells you the current state of put-call imbalance at a specific point on the volatility surface.
But current state isn't the question that matters! The question is: what's changing, and how fast!?
The Problem With 25-Delta Skew
The first problem is location. In typical crypto volatility environments, 25-delta options sit only 6-8% out of the money (OTM). These strikes represent standard hedging territory, i.e. the kind of positioning every institution maintains as baseline risk management. True tail events, the moves thatgenerate alpha or catastrophic losses, occur 15-20% OTM, in thedeep strike regions where extreme positioning reveals itself.
Traditional skew measures the wrong part of the distribution.
The second problem is static measurement. A single-point skew reading tells you where positioning sits right now. It doesn't tell you whether that positioning is accelerating, decelerating, or stable. When participants prepare for extreme moves, they don't proportionally increase all strikes! They accelerate into deep tails while maintaining standard hedges.
A 25-delta skew of 2.5 points could mean:
- Proportional positioning across the entire curve (standard hedging)
- Aggressive accumulation in deep tails while moderate strikes remain flat (tail event preparation)
- Moderate strike buildup with flat deep tails (routine flow)
Traditional skew can't distinguish between these scenarios. The number is identical. The market implications are opposite.
The third problem is regime dependence. Raw skew values are meaningless withoutvolatility context. A 3-point skew in a 40% volatility environment tells a completely different story than 3-point skew in a 120% volatility regime. Most analytics platforms report raw skew without normalization, forcing traders to mentally adjust for baseline volatility while making split-second decisions.
One can easily solve this, i.e. to normalize by volatility:
But even normalized single-point skew misses the acceleration question. You need two measurements to detect velocity. You need to measure both the deep tail and the moderate strikes, then calculate their divergence.
Building Tail Strike: Measuring Acceleration, Not Position
We built Tail Strike™ to solve three problems simultaneously: measure the right strikes, detect velocity rather than position, and achieve regime independence through normalization.
The conceptual framework operates on dual-region measurement. Instead of examining a single point on the volatility surface, Tail Strike compares two distinct zones:
- Deep Tail Zone: Far OTM strikes 15-20% from spot, where tail events actually materialize
- Moderate Strike Zone: Standard hedging territory 6-10% from spot, representing typical institutional positioning
At each zone, we calculate traditional skew, the put-call implied volatility differential. Then both measurements get normalized by current volatility to remove regime bias. The critical insight emerges when you calculate the divergence between these normalized measurements:
The exact functional form remains proprietary, but the principle is straightforward. When deep tail positioning builds at the same rate as moderate strikes, the metric reads near zero: a proportional flow, standard hedging, nothing unusual. When deep tail positioning accelerates faster than moderate strikes, the metric spikes positive for puts or negative for calls. That acceleration signals tail event preparation.
The normalization by volatility ensures regime independence. A Tail Strike reading of 0.15 carriesidentical interpretation whether baseline volatility sits at 40% or 120%! You can compare signals across different volatility regimes, across different assets, across different time periods. The metric measures relative acceleration, not absolute positioning.
Empirical observation from Bitcoin and Ethereum markets reveals clear signal thresholds:
- < 0.08: Normal proportional positioning
- 0.08 < ≤ 0.15: Moderate tail acceleration
- 0.15 < ≤ 0.20: High tail acceleration
- > 0.20: Extreme tail positioning
Statistical analysis shows that 90% of readings fall within the normal range. Moderate signals occur 8-12% of the time. High and extreme signals combined represent less than 5% of observations, i.e. precisely the frequency you want for actionable edge.
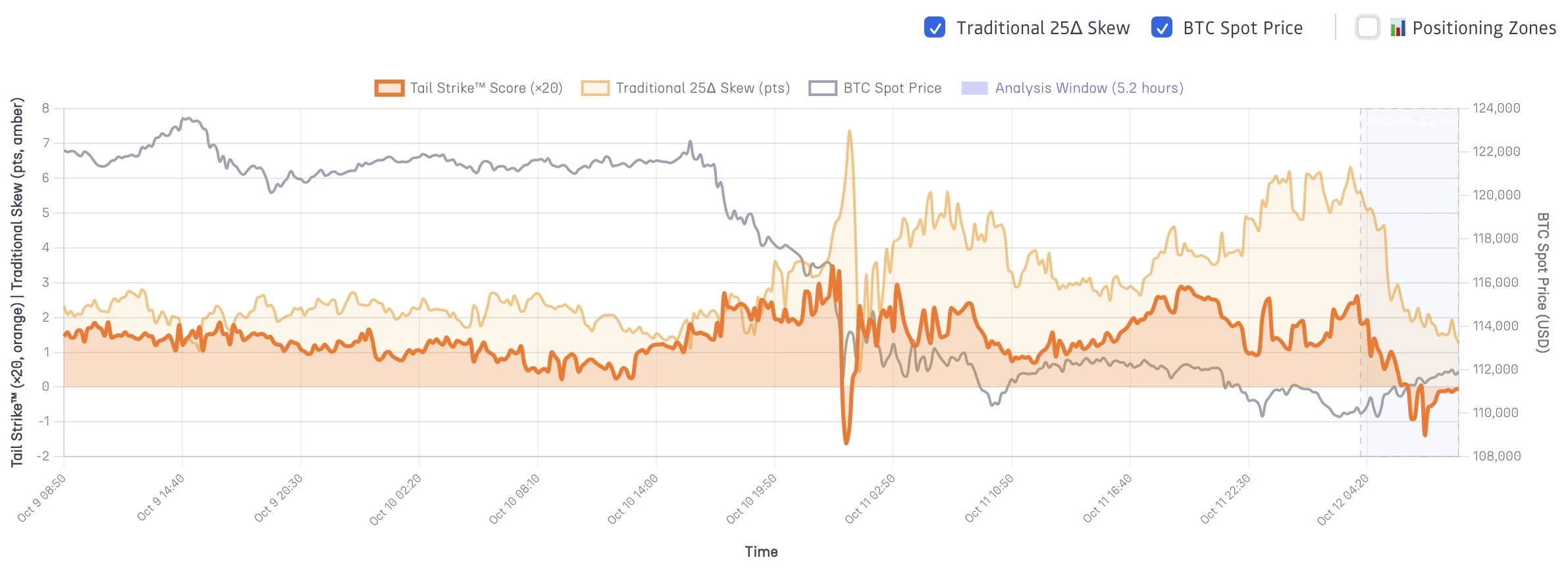
Figure 1: Tail Strike™ vs Traditional Skew Time Series
Shows Tail Strike score (orange line, ×20 scale), traditional 25-delta skew (tan line, points), and BTC spot price (gray line). The analysis window (blue shading) highlights periods where Tail Strike detected acceleration that traditional skew missed entirely. Note how Tail Strike spikes precede price moves by 2-6 hours while traditional skew remains flat.
Real Market Validation: October 2025
Let's examine what actually happened during early October 2025, using the data visible in Figure 1.
Early October 9 through morning of October 10:
Bitcoin traded around the $122,000-124,000 level, visible as the gray line on the left side of Figure 1. Traditional 25-delta skew hovered between 2 and 3 points throughout this period. The tan line shows steady, unremarkable readings. Nothing in traditional metrics suggested preparation for a significant move.
Traditional analysis would call this environment neutral to slightly bearish. The 2-3 point skew represents modest put bias, typical for crypto options markets. Most traders would maintain existing positions, perhaps add light hedges, but no urgency.
Now examine the Tail Strike™ pattern through this same period.
The orange line (remember, displayed on ×20 scale) oscillates between 1.0 and 2.0 through early October 9 and into October 10 morning. Actual Tail Strike values: 0.05 to 0.10. This puts readings at or slightly above our 0.08 moderate threshold—elevated but not extreme. Some acceleration into deep tails occurring, but not yet reaching high-signal territory.
The critical move began around midday October 10.
Bitcoin dropped sharply from approximately $118,000 to $112,000 within hours, visible in Figure 1 as the steep gray line decline around the October 10 12:30 timestamp. Then continued falling toward $110,000 by late October 10. A total decline of roughly 10% from the $122k peak to the $110k bottom.
What did traditional skew do during this entire sequence?
Look at the tan line in Figure 1. It stayed between 2 and 3 points from October 9 through the entire October 10 decline. Completely static. The measurement that's supposed to indicate fear and tail hedging showed essentially no change as Bitcoin dropped 10%. You couldn't distinguish pre-move conditions from normal baseline positioning.
The Tail Strike readings tell a different story.
While elevated readings in the 1.5-2.0 range (×20 scale, or 0.075-0.10 actual) appeared through October 9-10, these moderate signals indicated positioning was building beyond typical hedging. Not extreme acceleration, but enough divergence between deep tail and moderate strikes to suggest institutional preparation for movement.
The regime-normalized framework reveals what raw skew obscures: deep tail strikes were accumulating faster than the moderate strikes that dominate traditional 25-delta measurements. That velocity divergence, i.e. the gap between how fast institutions were moving into far OTM strikes versus their standard hedging positions, signaled elevated move probability.
Reading the progression through October 9-10:
- Early Oct 9 (BTC ~$124k): Tail Strike 0.05-0.07, normal conditions
- Oct 9 afternoon through Oct 10 morning: Tail Strike 0.08-0.10, moderate signal territory
- Oct 10 midday onward: 10% decline materializes over following hours
Traditional skew provided no advance indication. The tan line shows identical 2-3 point readings before, during, and after the move. Static measurement, static information, no actionable edge.
Figure 2 makes the positioning dynamics even clearer through automatic classification overlays:
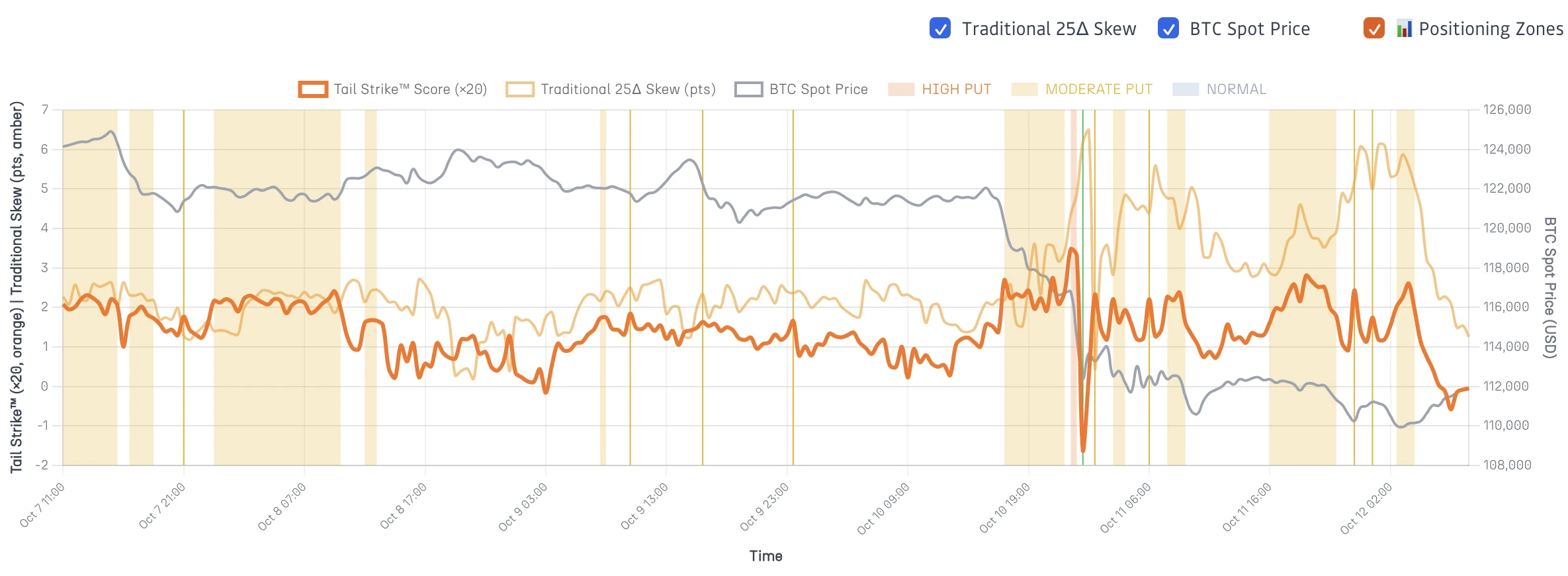
Figure 2: Positioning Zones Classification
Same time series with automatic positioning classification overlays. Orange zones indicate elevated or high tail acceleration (deep tail positioning building faster than moderate strikes). Yellow zones show moderate tail acceleration. Gray represents normal proportional flow. Vertical lines mark exact timestamps of classification changes. This visualization makes pattern recognition immediate, e.g. orange zones highlight when institutional positioning character changes, signaling heightened probability of tail events rather than guaranteeing directional moves.
To understand why Tail Strike detected what traditional metrics missed, examine how the calculation components decompose during actual market conditions.
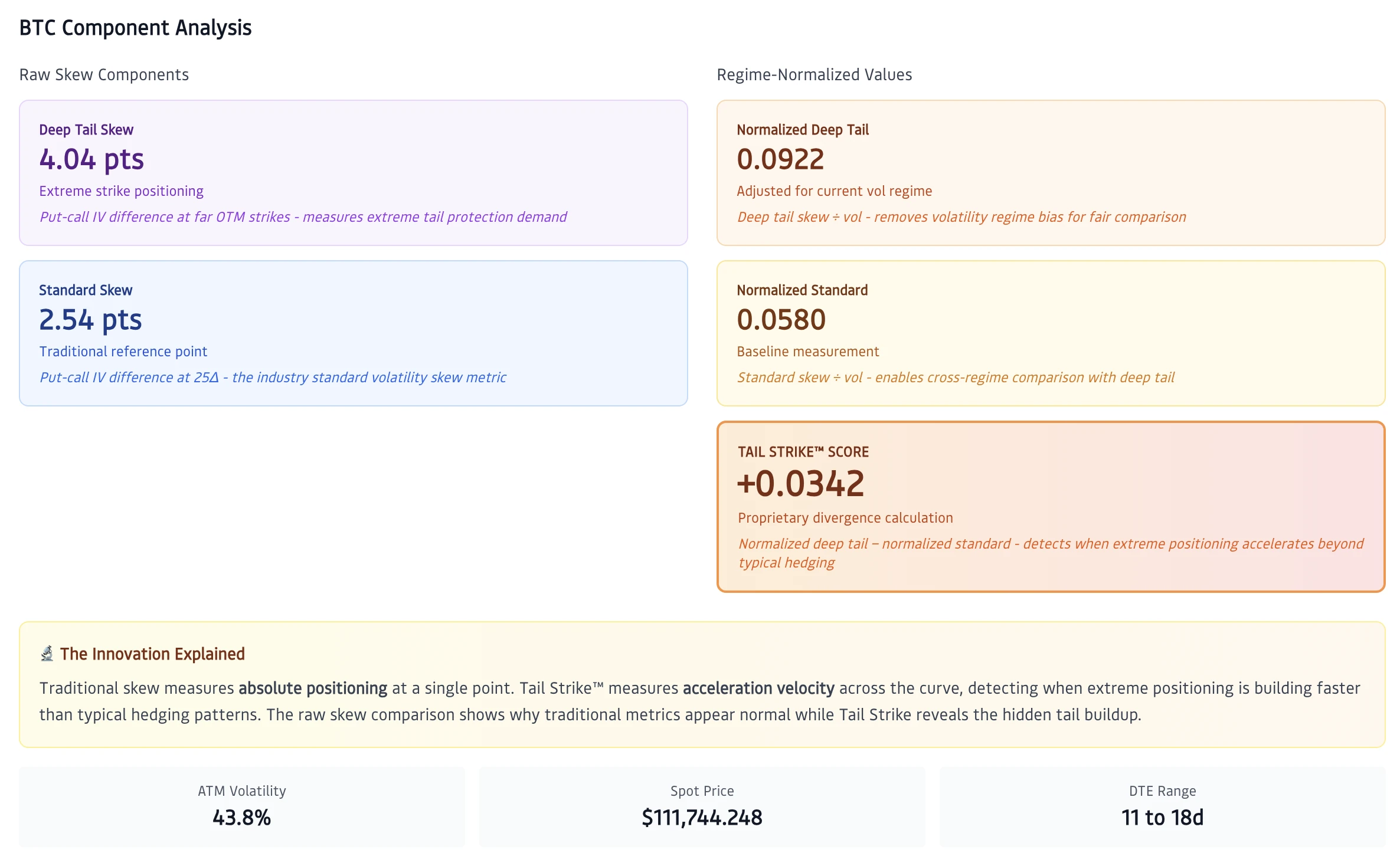
Figure 3: Component Analysis Breakdown
Shows the calculation components for a single timestamp. Left side displays raw skew components: Deep Tail Skew in purple showing extreme strike positioning, and Standard Skew in blue as the traditional reference point. Right side shows regime-normalized values dividing each by volatility. The Tail Strike™ score appears in orange, calculated from the divergence between normalized measurements. This decomposition reveals how traditional skew can appear normal while hidden tail acceleration builds.
Figure 3 breaks down the mechanics at a single point in time. The left panel shows raw skew values: Deep Tail Skew (purple) measures put-call IV differential at far OTM strikes, while Standard Skew (blue) represents the traditional 25-delta measurement.
The right panel reveals what normalization uncovers. After dividing each measurement by volatility (which was running around 44% during this period), the normalized values show relative positioning independent of the volatility regime. When normalized deep tail acceleration exceeds normalized moderate strike positioning by a meaningful margin, tail event preparation emerges from the data.
The orange Tail Strike™ score represents this divergence. Even when raw skew values look unremarkable or inverted, normalized measurements can reveal significant tail acceleration. This is precisely what happened in early October, i.e. traditional metrics saw routine positioning, while Tail Strike detected institutional preparation for the move that followed.
The ability to make direct cross-asset comparisons regardless of volatility regime represents a significant analytical advancement. You can instantly identify whether tail positioning is market-wide or concentrated in specific assets. You can track positioning across wildly different volatility environments. You can compare current readings to historical patterns spanning months or years of data.
Figure 4 demonstrates how signal frequency creates actionable edge rather than noise.
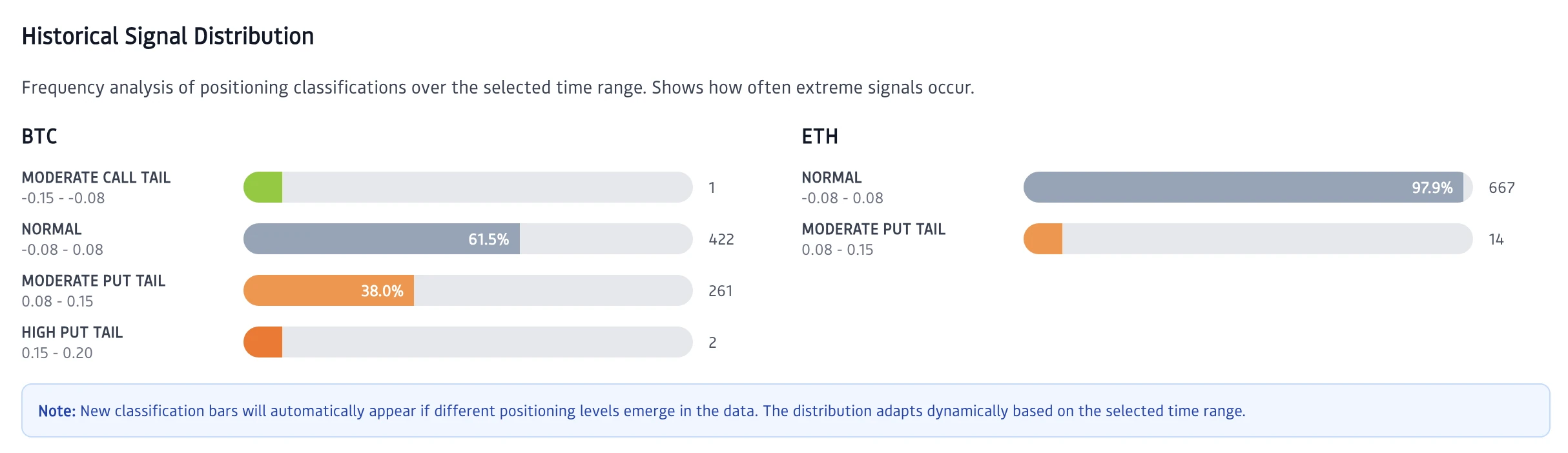
Figure 4: Historical Signal Distribution
Frequency analysis of positioning classifications over extended time periods. BTC distribution shows majority normal readings with approximately 38% showing moderate tail positioning, 2% elevated signals, and rare extreme events. ETH distribution shows 98% normal readings with only 2% moderate signals, reflecting ETH's typically more balanced options flow. The scarcity of high and extreme signals (combined <5% frequency) ensures actionable edge rather than noise. Note how each asset maintains distinct distribution patterns reflecting their unique market microstructure.
The distribution analysis in Figure 4 reveals why Tail Strike provides edge. BTC shows elevated signals roughly 38% of the time in moderate range, with only 2% reaching high territory and rare extreme readings. This frequency creates actionable timing. Signals occur often enough to matter, but rarely enough that each one demands attention.
ETH's distribution differs markedly: 98% normal readings with just 2% moderate signals. This reflects Ethereum's characteristically more balanced options flow. The distinct patterns across assets enable sophisticated relative positioning strategies. When BTC shows elevated Tail Strike while ETH remains normal, you're observing BTC-specific concerns rather than systemic risk.
Why This Changes Everything
The implications extend beyond better prediction accuracy. Tail Strike fundamentally changes how you think about options positioning in crypto markets.
First: Detection speed. Traditional skew reacts to positioning changes after they've fully materialized. By measuring deep tail acceleration relative to moderate strikes, Tail Strike detects buildups earlier in their development. The 2-6 hour lead time provides actionable windows for position adjustment, hedge implementation, or strategic entry.
Second: Signal clarity. Traditional skew generates continuous readings across a wide range. You're left interpreting whether 2.3 points is significant or if you should wait for 2.8 or 3.5. Tail Strike's normalized framework creates natural thresholds. Readings below 0.08 represent baseline. Readings above 0.15 demand attention. The interpretation is unambiguous.
Third: Regime independence. You can finally maintain consistent interpretation across different market conditions. A high-signal reading in January 2025's low-volatility environment carries the same weight as a high-signal reading in March 2024's elevated volatility regime. Your decision framework remains stable even as market character changes.
Fourth: Asset comparison. The ability to directly compare positioning across Bitcoin, Ethereum, and eventually SOL and XRP using a single normalized metric eliminates the mental overhead of tracking multiple context-dependent measurements. You can instantly identify where institutional concern is concentrated.
The mathematical elegance comes from solving multiple problems with a single framework. By measuring divergence rather than absolute position, by normalizing for volatility regime, by focusing on the strikes where tail events actually occur, Tail Strike converts noisy options flow into clear positioning signals.
We built Tail Strike because crypto options markets needed measurement tools designed for their unique characteristics rather than tools borrowed from equity markets and hoped for the best. The validation comes not from theoretical models but from live market performance. The signal works because it measures what matters, i.e. acceleration into extreme strikes backed by institutional capital.
Every 10 minutes, our systems calculate fresh Tail Strike readings for Bitcoin and Ethereum, analyzing positioning across thousands of strikes to detect patterns that traditional metrics miss entirely. The calculations run automatically, the thresholds remain consistent, the interpretation stays clear.
This is, as we believe deeply, the new standard for crypto options positioning analysis. Traditional 25-delta skew tells you where the market sits. Tail Strike™ tells you where it's going.
Technical Note: Tail Strike™ currently operates in production for BTC and ETH with 95%+ signal confidence backed by institutional liquidity ($20M-$300M in deep tail regions). SOL and XRP development progresses as their options markets mature. Live monitoring available at our Cayo Crypto-Options Lab.
How to Trade Tail Strike?
Tail Strike provides probabilistic edge, not guaranteed outcomes. Here's how to translate signals into positions:
Signal-Based Position Sizing:
- TS 0.08-0.15 (Moderate): 25-50% of normal position size. Add light hedges, tighten stops, reduce leverage. These signals occur 8-12% of the time—treat as early warnings.
- TS 0.15-0.20 (High): 50-75% position size. Implement full hedging strategy. Expected 2-6 hour window for moves. Occurs 3-5% of the time.
- TS > 0.20 (Extreme): Maximum defensive positioning. Consider profit-taking on longs, full tail hedges, or directional shorts. Rare signals (<2% frequency) demand immediate action.
Confirmation Requirements:
Never trade Tail Strike signals in isolation. Require minimum $20M volume backing in deep tail strikes for HIGH confidence classification. Signals without volume backing represent lower probability setups, i.e. size accordingly or skip entirely.
Cross-Asset Divergence Plays:
When BTC shows elevated Tail Strike while ETH remains normal (or vice versa), you're observing asset-specific concerns. Consider relative value strategies: hedge the elevated asset, maintain exposure to the stable one. This approach isolates specific risk rather than exiting crypto exposure entirely.
Time Decay Awareness:
The 2-6 hour predictive window means signals lose relevance quickly. If Tail Strike elevates but no move materializes within 6-8 hours, re-evaluate. Markets can resolve tail positioning through time decay rather than price movement. Don't marry positions based on stale signals.
What NOT to Do:
- Don't over-trade moderate signals. 38% occurrence rate in BTC means you'll see many. Pick the best setups backed by volume and complementary technicals.
- Don't ignore when Tail Strike returns to normal (<0.08). This signals pressure release.
- Don't expect perfect timing. Tail Strike detects institutional positioning acceleration, not exact price tops/bottoms. Use it for risk management and sizing, not precise entries.
Practical Example: October 10 case study showed TS at 0.08-0.10 through morning hours. Appropriate response: reduce long exposure by 30-40%, add 10-15% downside put protection, tighten stops from -5% to -3%. When TS returned to normal range post-decline, that signaled re-entry opportunity. This approach would have limited downside participation while maintaining upside optionality.
Remember: Tail Strike measures institutional positioning velocity, not retail sentiment. When signals trigger, sophisticated players are already positioning. Your edge comes from detecting this earlier than traditional metrics allow. Use that window wisely.
Risk Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency options trading involves substantial risk and may not be suitable for all investors. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article provides initial analyses for informational purposes only(!) and should not be considered as a financial advice! Please consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Tail Strike™ and how does it differ from traditional skew metrics?
Tail Strike™ measures the divergence velocity between deep tail strikes (far out-of-the-money) and moderate strike positioning, normalized by volatility. Unlike traditional 25-delta skew that provides a single static measurement, Tail Strike detects acceleration patterns revealing when institutional players are building positions for extreme moves beyond typical hedging.
Why doesn't traditional 25-delta skew work well for cryptocurrency options?
Traditional 25-delta skew was designed for equity markets with unidirectional crash risk, stable delta reference points, and slow regime changes. Crypto markets exhibit bidirectional volatility, rapid intraday delta shifts, 24/7 continuous trading, and volatility regimes that change in hours rather than weeks. Delta reference points can shift dramatically within hours following significant price moves.
What does a high Tail Strike™ score actually tell traders?
A Tail Strike score above 0.15 indicates that deep tail positioning is building significantly faster than moderate strike positioning after regime normalization. This reveals institutional acceleration into extreme strikes, typically 2-6 hours before corresponding price moves. Scores above 0.20 represent critical divergence backed by institutional volume.
How is Tail Strike™ regime-independent?
By normalizing both deep tail and moderate strike skew measurements by current volatility, Tail Strike removes baseline volatility regime bias. A score of 0.15 carries identical interpretation whether ATM volatility is 40% or 120%, enabling direct comparison across different market conditions and assets.
Related Articles
Bitcoin Gamma Walls: When Math Meets Market Reality
We dive into Bitcoin options gamma exposure which reveals a surprising disconnect between theory and practice. With aggregate GEX representing just 0.03% of daily trading volume, are 'gamma walls' actually walls or just speed bumps?
BTC vs ETH Options: The Execution Quality Revolution - Why Both Markets Just Got Much Better
Our upgraded comprehensive analysis reveals a dramatic transformation in crypto options execution quality. Both Bitcoin and Ethereum options now offer significantly tighter spreads and more efficient trading opportunities, though ETH maintains its execution advantage.